A Non-Developer’s Guide to Base64 and URL Encoding (And When You Actually Need Them)
You’ve probably seen weird strings full of %20 or long blobs of letters and slashes. That’s encoding. Here’s the plain-English version of what’s going on and how to do it without writing code.
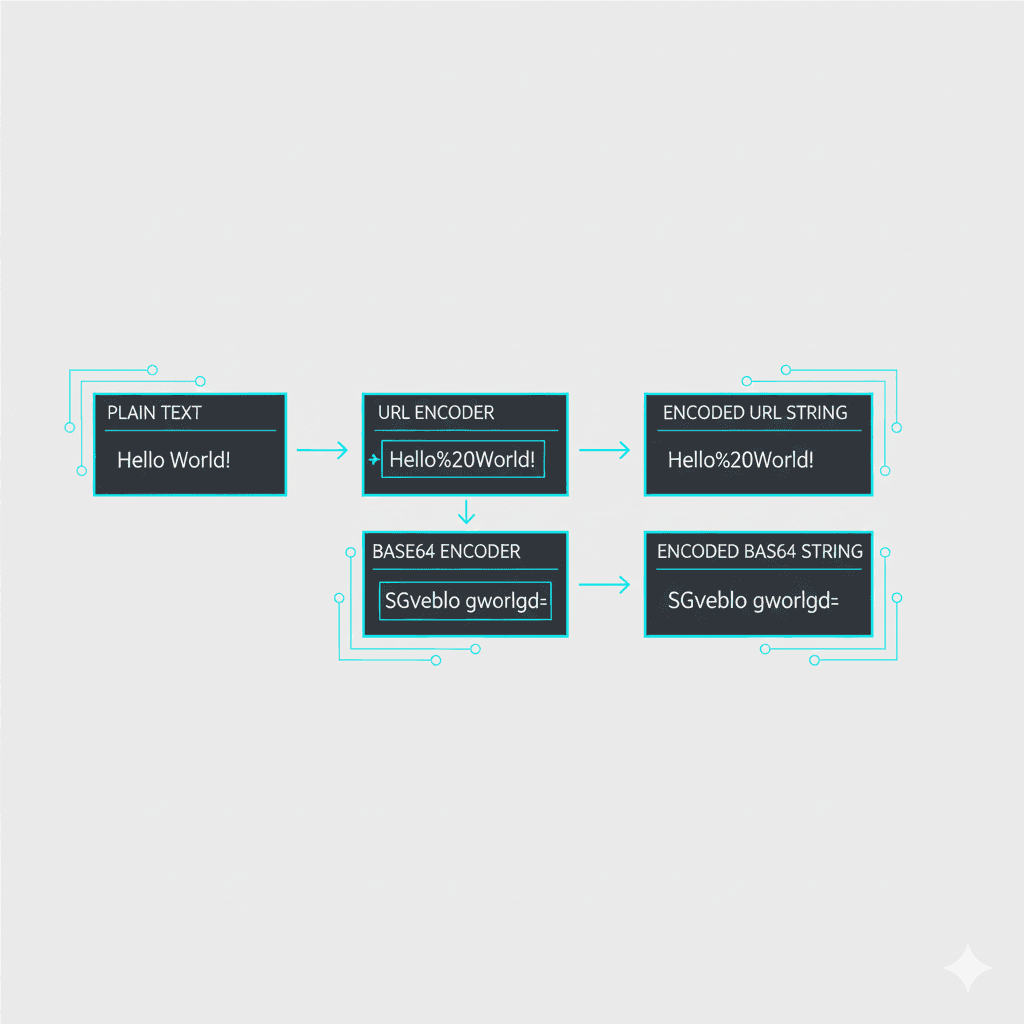
URL encoding in 60 seconds
- URLs can only safely include certain characters (letters, numbers, a few symbols).
- Spaces and special characters get turned into codes like
%20. - Use it when sharing links with spaces, punctuation, or non-Latin characters.
Quick URL encoding steps
- Copy your text with spaces or accents.
- Paste into TiniText URL Encode/Decode.
- Click Encode; copy the safe URL string.
- If you see a
%mess and need it human-readable, click Decode.
Base64 in 60 seconds
- A way to represent binary data (images, files) or text using only safe characters.
- Common in emails, config files, small embedded images, and API payloads.
- Not encryption—just representation.
Quick Base64 steps
- Paste a short snippet (or tiny image as data) into TiniText Base64 Encode/Decode.
- Click Encode to get the Base64 string.
- To read a Base64 string, click Decode and review the output.
Note: Base64 strings get ~33% larger than the original data. Keep payloads small.
Everyday use cases
- Sharing config snippets: Turn JSON with quotes into a single safe string.
- Debugging API calls: Decode Base64 fields in responses to see what’s inside.
- Embedding icons: Tiny SVGs can be Base64-encoded in CSS or HTML for quick prototypes.
- Cleaning URLs: Encode subject lines or search queries so links don’t break.
Where you’ve seen it
%20in links is URL encoding.- Email attachments use Base64 behind the scenes.
- Data URLs like
data:image/png;base64,...embed small images.
How TiniText helps
- URL Tools: Encode/decode instantly without touching a terminal.
- Base64 Tools: Encode/decode short snippets to see what’s inside.
- Text Cleaner + Diff: When copying payloads between tools, clean them and compare before/after to avoid mistakes.
Other tools (when you need more)
- Postman or Insomnia for API workflows.
- VS Code with REST client extensions.
- Browser devtools Network tab to inspect requests.